You must have seen black & white square-shaped barcodes on products, hoardings, and newspapers. These are QR Codes.
In fact, QR Code usage is on the rise. According to Bluebite, the following trend was reported from 2018 to 2020:
96% growth in QR Code Reach
94% surge in the number of interactions
98% growth in the number of interactions per active object
This data clearly conveys an increase in QR Code reach and its usage over the years.
Moreover, various apps such as Whatsapp and Instagram use QR Codes as a feature to add friends. And brands like Coca-Cola are using QR Codes as a marketing tool to attract new customers. Moreover, retailers such as Walmart use QR Codes to accept payments. Impressive, isn’t it?
It’s difficult to imagine how a simple tool like QR Code can do so much. But how did they come into existence?
We need to take a short trip down history and first understand the development of Barcodes.
Barcode – the predecessor to the QR Code
The year was 1948. Location: Pennsylvania, US.
Graduate student Bernard Silver overheard his Dean and the President of a local store.
The discussion was about creating a technology that could read product information during checkout. This, would cut down human errors and relieve the workers from the pain of manual data entry.
After a few tests, Bernard and his friend Norman Joseph Woodland created the first Barcode.
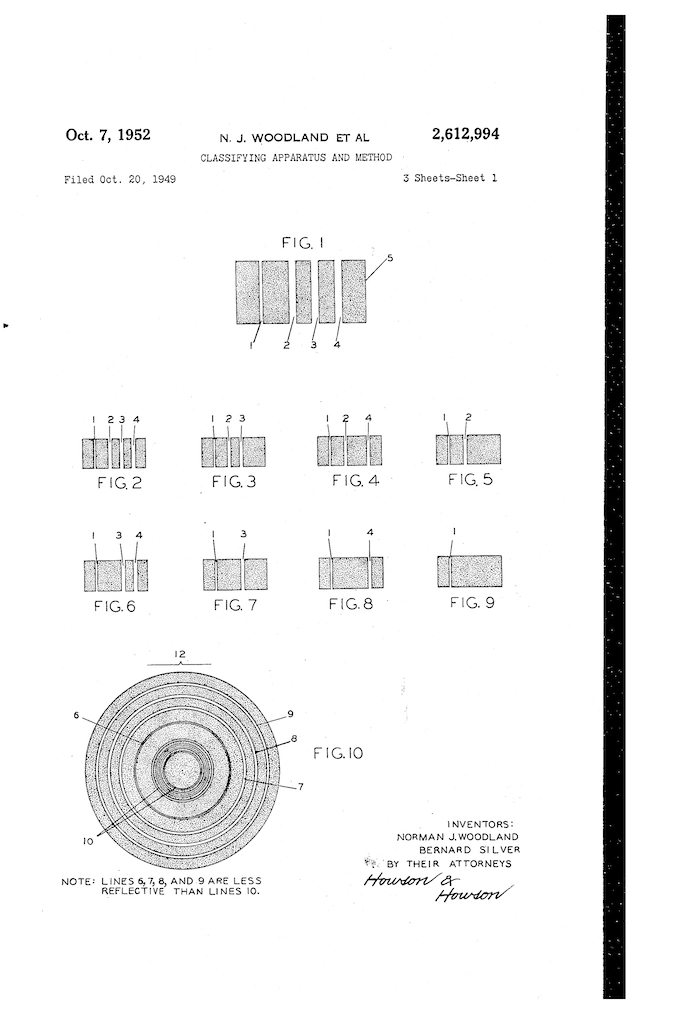
By the late ’70s, Barcode became an integral part of inventory management. Particularly in retail and automobile manufacturing.
In the early ’80s, the Universal Product Code (UPC) was released. UPC are unique Barcodes assigned to products. These allow retailers to manage common products with ease.
The invention of the Barcode made lives easy. Yet, it had certain limitations.
Limitations of Barcodes
a. Unidirectional: Barcodes are one dimensional (1D) and store data in one direction only. If the Scanner is not aligned in that direction, the barcode will not scan
b. Storage Capacity: Barcodes can store up to 20 characters only
c. Size: More the characters, the longer the Barcode. Printing a long barcode on a small product is a challenge
d. Vulnerable: Barcodes stop working when affected by dirt or damage
e. Encoding: Barcodes can only encode alphanumeric characters
2D Barcode – Advanced version of Barcodes
To overcome the limitations of Barcodes, development on 2D Barcodes began.
In 1987, David Allais developed the first 2D Barcode. Even this code has its limitations but it was the predecessor to the popular PDF417.
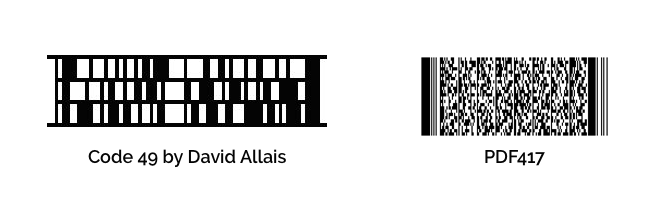
Soon QR Code, Aztec Code, DataMatrix, Nex Code, and many other 2D Barcodes entered the market. Unlike 1D barcodes, these were compact and could store more data.

Most 2D Barcodes remain proprietary and thus failed to achieve mass adoption.
QR Codes – The Superhero Barcode
The year 1994.
Toyota was not happy with the Barcodes used in their automobile factories. They wanted more speed and an error-free assembly line. The company assigned its sister concern Denso Wave to come up with a solution.
It was Masahiro Hara from Denso Wave who developed the Quick Response Code or QR Code.

- Denso Wave decided to make the specifications of the code public so anyone was free to use it. The company still holds the patent rights but decided not to exercise them. This move allowed widespread adoption of the technology.
QR Code was first used in automobile, pharmaceutical, and retail industries to track inventory. They are now used for marketing, social media, and security applications as well.

Advantages of QR Codes over Barcodes
a. Storage Capacity
QR Codes can store up to 7,089 numeric characters (without spaces). This translates to 2,953 alphanumeric characters with spaces and punctuation. This amount is more than enough for most use cases.
b. Smaller Size
For the same data encoded, a QR Code takes up less space compared to a Barcode. Hence, QR Codes are especially better when the printing space is a constraint.
c. Orientation
A QR Code is scannable from any angle—360 degrees scannable. With it, end-users don’t need to hold the QR Code or scanner in a pre-defined manner. This is unlike barcodes which can only be scanned in one direction.
While you know barcodes require dedicated handheld scanners, QR Codes can be scanned with the smartphone in your pocket. Convenient, right?
To do it, you just need to open the camera application on your smartphone. And hold it in front of the QR Code. You’ll receive a notification if it gets scanned.
In case it doesn’t, you can install third-party QR Code scanning apps such as QR Reader, QR and Barcode scanner, QR and Barcode Reader, from the Play Store or App Store
d. Diversity in encoded data
QR Codes can encode numeric, alphanumeric, binary, and even Kanji characters. Hence, you can easily encode Website URLs, documents, multimedia files, or even simple text into them.
e. Error Correction
QR Codes come with a feature called error correction. It ensures that QR Codes remain scannable even after getting damaged, distorted, or dirty by up to 30%
f. Password Protected
You can password protect your QR Code against any unauthorized scan. This feature is exclusive to Dynamic Codes. Admin can set a password while creating a QR Code. When scanned, the end-users will be prompted to enter the required password to be able to access the encoded data.
Related : Best QR Code Generator
Future of Barcoding
Well, the future of barcoding is here. And here are some interesting features that will surely blow your mind:
1. Make end-users take the desired action
QR Codes can help you make the end-users take desired actions such as:
- Driving people to your website
- Showing documents
- Redirecting end-users to a mobile-optimized landing page containing buttons linked to all your social media profiles
- Redirecting the end-users to a particular app in the respective App Store based on the device’s OS
- Helping you share your contact information with an option—Save as Contact
- Offering detailed event information with an option to RSVP
- Helping your audience listen to an audio file
- Giving complete product information
Depending on what actions would you like the end-users to take, you can select the desired QR Code category. And go-ahead to create the QR Code of your choice.
2. Scan Tracking
QR Codes come with a complete package of tracking and analytical abilities. Here’s how:
QR Codes allow you to track their entire scanning activity. That means you can track the scans with respect to the following parameters:
- Date and time
- Location
- Device
- Browser
- Operating system
QR Codes also offer event tracking. It helps you analyze how your end-users interact with the encoded content after they scan the QR Code. It could be a button for sign-up or registration.
3. Custom-Design feature
You can add design to the QR Code without affecting scannability. There are two design options:
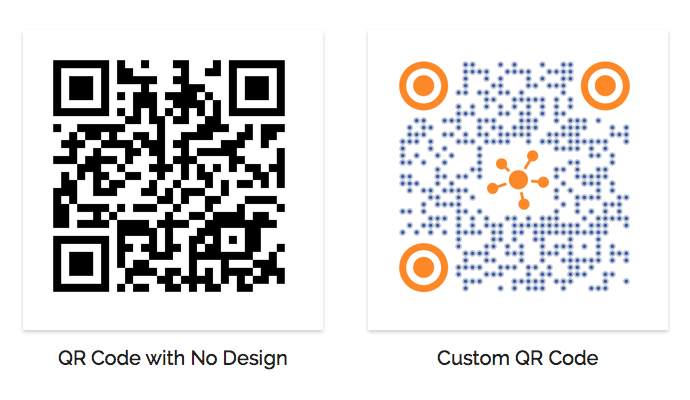
a. Custom logo design
In this option, you can add a logo to your QR Code. You can even change the color and pattern of both the data modules and the eyes. In fact, you can also add an appropriate gradient to the data modules’ color.
b. Custom background design
This option allows you to add an image as QR Code’s background. Here, you can also change the pattern of both the QR Code’s eyes and the data modules.
In case you are interested in how to create custom QR Codes, here is a detailed guide on it.
This custom design allows marketers to add QR Codes to their marketing campaigns.
Popular apps like Snapchat, WhatsApp, Instagram, and PayTm have taken this to a new level. They have deviated from the QR Code standard and are using codes customized to their brand.

4. Ease of creation
QR Codes are very simple to create. All that you need is a QR Code generator that offers you the desired QR Code category and features.
QR Code Alternatives
Riding on the popularity of QR Codes, Denso Wave has now developed advanced versions. There are Micro QR Code, iQR Code, SQRC, and Frame QR.
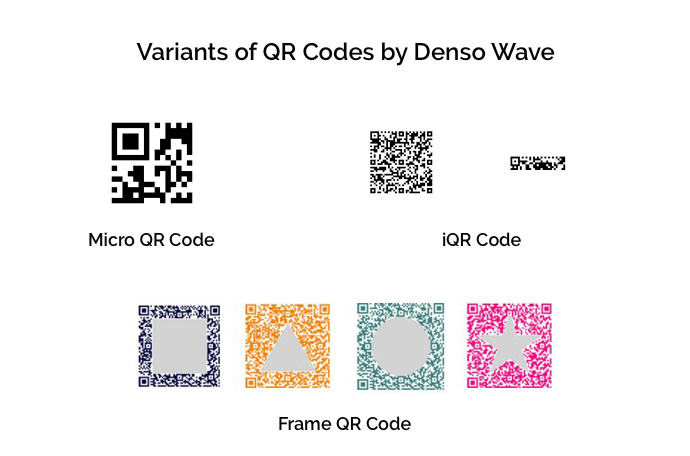
While these are superior in technology, they are not a public domain like QR Codes.
Some marketers claim that Augmented Reality and NFC are the future of offline-to-online marketing. But I beg to differ.
No doubt these technologies are superior to the QR Code. But they are neither affordable nor universal. For example, NFC only works over short distances around 10 cm. Also, for the AR campaign, users need to download a new app.
Similarly, different face angles can throw off image recognition’s reliability.
The bottom line is technology has advanced but QR Code has held its fort since 1994.
That’s it. That is all you need to know about QR Code history.

Thanks, nice post
Thank you for this easy intro article
We’re glad you found the article helpful.