Don’t know what is a QR Code or how businesses use them? Don’t worry. In this exhaustive guide, we have covered the basics of QR Code technology. We update our page often so don’t forget to add us to your bookmarks.
Read this ultimate guide to learn all about QR Codes
A. What is a QR Code?
A Quick Response Code is a popular type of two-dimensional barcode. It encodes alphanumeric information. To decode this, you can either use a handheld scanner or even a QR Code scanning application on your smartphone.
Did you know?
QR Code scans surged by 57% globally in 50 countries and an impressive 8 QR Codes are generated per minute, showcasing widespread adoption.
Source: ProfileTree
In fact, many smartphones such as iPhone, Xiaomi, Motorola, and Samsung now have an in-built QR Code scanning feature in their stock camera application.
A Japanese company, Denso Wave Corporation, developed Quick Response Codes in 1994. Their role was vehicle tracking and high-speed component scanning in the automobile industry.
Now that you know what is a QR Code, let’s take a look at how they work. Keep reading!
B. How do QR Codes work
If you look at a QR Code, you’ll see black-colored squares (or dots) all over it. These are called data modules. The information you add to the QR Code is stored in these data modules.
Hence, every module (black or white unit block) or a string of modules either represents data or a function.
So what scanners do is—they start reading these data modules to decode the information stored in them to show the stored data to the users.
The illustration below depicts how a QR Code scanner decodes a QR Code:
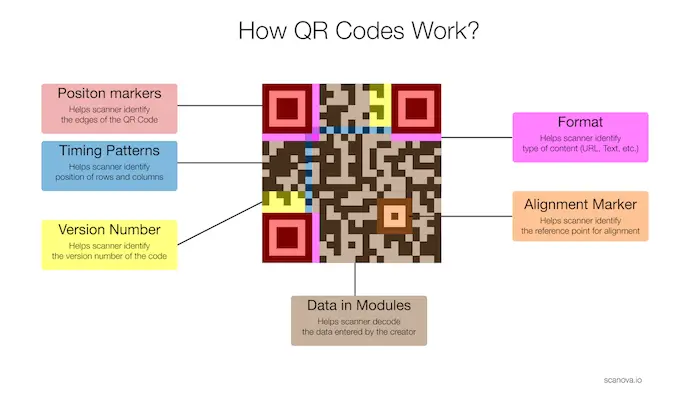
Here’s a detailed guide on how QR Codes work.
Many users have some common questions before getting started with QR Codes. And you may have them too. Let’s go through these in detail:
C. Most common QR Code FAQs
1. What does a QR Code mean?
QR stands for ‘Quick Response’. Hence, the QR Code becomes a Quick Response Code.
And the reason behind this name is pretty simple. Have you ever scanned a QR Code? You might have done it most probably. In case not, try scanning one now.
It’ll hardly take a second or two for you to do the needful and see the content in the QR Code. Quick, right?
That’s exactly the rationale behind the name. Since a QR Code gets scanned in no time (response quickly), hence, the name.
2. How many times can my QR Code be scanned?
Technically, as many times as you want.
Static QR Codes, which are permanent in nature, come with unlimited scans. Once created, they can’t be deactivated. In addition, even your QR Code generator can’t limit the number of scans on them.
However, due to their limited functionality, static QR Codes aren’t really the most sought-after.
Dynamic QR Codes, on the other hand, may or may not have unlimited scans. It totally depends on your QR Code generator. Service providers such as Scanova don’t put a limit on the scans your QR Code can get.
In addition, since the dynamic ones are both editable and trackable, they’re preferred way more than the static ones. Watch this quick video for a detailed comparison of static and dynamic QR Codes.
Did you know?
26.95 million QR Code scans were recorded globally in 2022-2023. According to the study, a 22% increase in QR Code usage is expected across regions by 2025.
Source: ProfileTree
3. Does a QR Code work forever?
As mentioned before, a static QR Code is permanent in nature and, hence, works forever. But that is not the case with a dynamic QR Code.
For a dynamic QR Code to work, you need an ongoing subscription with your QR Code generator.
4. Who is a QR Code relevant for?
There’s no specific job role, industry, department, or use case that QR Codes are relevant for. In fact, it’s the quite opposite. QR Codes are so versatile that everyone is using them.
From ads and promotions to operations, they fit everywhere. For example, in 2022, they were used by Dunzo, an instant delivery app in India, used a QR Code to promote its app. The response was so good (and unexpected) that the app crashed due to traffic overload.
On the other hand, many logistics companies use QR Codes for inventory management. Since QR Code store way more data than barcodes and are damage-resistant, they work amazingly well.
5. Can I add a design to my QR Code?

Yes, you can add a design to your QR Code. And by that, we don’t mean that you need to hire a graphic designer. Advanced QR Code generators such as Scanova offer this capability.
This feature helps you make your QR Code visually appealing in no time. Isn’t that great?
6. What is the meaning of QR Code Security?
QR Codes themselves are inherently secure, but their security depends on how they are used. The security risk lies in where the QR Code leads you. Malicious elements can create QR Codes that link to phishing websites designed to steal your information, malware-laden downloads, or even fake login pages.
QR Code security is simply the process of making QR Codes secure. Let’s see how you can make your QR Codes more secure:
- Be Wary of Unknown Sources: Only scan QR Codes from trusted sources. If you see a random QR Code plastered on a streetlamp, it’s best to avoid it.
- Verify the Link Before Clicking: Many QR scanner apps allow you to see the URL encoded in the QR Code before visiting it. Double-check the link for suspicious characters or typos before clicking.
- Use a Secure QR Code Scanner: Some scanner apps offer additional security features like checking the URL against known malware databases. Consider using such apps for added peace of mind.
Scanova’s Tip: We recommend using Kaspersky’s QR Code reader, which includes built-in security to prevent suspicious behavior. It also guards against viruses and questionable URLs, ensuring a safe experience for iOS and Android users.
7. Are QR Codes secure for encoding sensitive information?
Choosing a secure option is very important when sharing sensitive information, like business documents or confidential files. Look for service providers prioritizing data privacy and adhering to industry-recognized compliance standards like GDPR, SOC 2, and ISO 27001.
These certifications demonstrate a provider’s commitment to robust security practices, offering peace of mind when trusting them with your sensitive data.
Understanding the Certifications:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This is a European Union regulation that governs how personal data is collected, stored, and used. A GDPR-compliant provider ensures your data is handled with strict controls and user privacy is respected.
- SOC 2 (System and Organization Controls): A SOC 2-compliant provider demonstrates they have robust controls in place to safeguard customer data, including security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System): Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO 27001 outlines a framework for establishing and maintaining an information security management system (ISMS).
An ISO 27001-compliant provider has a systematic approach to managing information security risks, ensuring your data is protected throughout its lifecycle.
8. Why does privacy compliance matter when choosing a QR code generator?
Choosing a service provider with these certifications signifies their dedication to data security. Here’s why it’s important:
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: Compliance standards minimize the likelihood of data breaches and unauthorized access to your confidential information.
- Enhanced Data Privacy: These regulations and frameworks put user privacy at the forefront, ensuring your data is handled ethically and according to strict guidelines.
- Improved Transparency: Compliance certifications demonstrate a provider’s commitment to transparency. You gain confidence knowing they take data security seriously.
- Regulatory Compliance: Depending on your industry or location, complying with data privacy regulations might be mandatory. Choosing a compliant provider helps you avoid any legal ramifications.
In short, opting for a service provider that prioritizes data security and adheres to GDPR, SOC 2, and ISO 27001 standards gives you peace of mind. You can share confidential data with the assurance that it’s protected by industry-recognized best practices.
Looking for a Secure Option?
Scanova, a product of Trycon, sets the bar too high when it comes to privacy. It prioritizes user privacy and adheres to GDPR, SOC 2, and ISO 27001:2013 standards. This can be a secure option for your confidential data-sharing needs.
Read more here: Trycon’s Data Security & Compliance

9. How to avoid misuse of data when using QR Codes?
Prevention is better than cure. Likewise, you can avoid the misuse of information and data by following the precautions mentioned below:
- Don’t Encode Sensitive Information: Avoid embedding sensitive data like passwords or credit card details directly into QR Codes. These codes can be intercepted, and the information could fall into the wrong hands.
- Use Short URLs: QR Codes have limited data storage capacity. Using a link shortener can help, but ensure the shortening service is reputable. Scanova offers the creation of QR Codes with dynamic short URLs that are secure. Also, you can replace Scanova’s standard short URL (e.g., https://scnv.io/AbCd) with a personalized URL (e.g. https://scnv.io/cafemenu or https://qr.cafe.com/menu).
- Password Protect Encoded Data (if necessary): If you must encode sensitive information, consider using a QR Code generation tool like Scanova that allows password protection. This adds an extra layer of security, requiring a password to access the encoded data.
Scanova’s Tip: You control what information you share through QR Codes. By following these tips and practicing caution, you can leverage the convenience of QR Codes without compromising your security.
In case you didn’t get your queries answered, let us know in the comments.
Ready to move on to the next section? Let’s move ahead.
D. What are QR Codes used for
Since 1994, Quick Response Codes have come a long way. In the smartphone era, these square-shaped barcodes have found extensive applications.
Some of these include inventory management, marketing & advertising, security, mobile payments, education, and personal use.
Different industries are using them immensely. Statistics show that QR Code scanning was rampant across the world in 2018. And will continue to grow in 2019.
Did you know?
Toyota’s use of QR Codes helps them address a recall for defective Takata airbags. This significantly streamlined the process, making it more efficient for up to 70 million vehicles.
Source: MyQRCode
This implies that their use is soaring every day. These 2D barcodes store information such as webpage URLs, text, and contact information.
To view this information, you simply need to scan the code using an app on your smartphone. It’s even easier than clicking a picture.
QR Codes are so easy to use that anybody can create and use them for their benefit.
Today, they are commonly added to:
- Business cards to allow people save contact details
- Prevent the spread of COVID-19 by making contact tracing, PPE kits, and vaccination better
- Class material to engage and teach children
- Hire suitable candidates for the HRs and even get a job for the jobseekers
- Print advertisements to allow readers to visit the website, register for an event, etc.
- Share live locations for various use cases
- Mobile payment applications to make transactions
- Product packaging to allow consumers to get in-depth product information
- Make business processes such as sales and marketing better
- Event or travel tickets to authorize and log entry
- Make industries such as food and alcoholic beverages transparent for the customers
- Wedding invitations to make things easier for the guests
- Invitation cards to help guests get the venue location on their phone’s maps application
- Share and market your stories in various ways
- Encode a survey or form to get feedback
The list doesn’t end here. There are, in fact, many crazy and innovative use cases of QR Codes.
1. How to get the most out of QR Codes
If you use Google Adwords for search engine marketing, you must have an SEM expert. The expert’s job is to optimize CTR for most conversions.
Similarly, in offline-to-online marketing (QR Codes), you need to follow the best practices. You need to always ensure that the Quick Response Code:
- Is accessible to your target audience
- Is scannable
- Has clear instructions that tell the users what to do or what to expect after scanning it (e.g., “Scan me to register”)
- Is placed in an area with a cellular network
- Leads to a mobile-optimized landing page
- Is downloaded in a high-resolution format such as SVG or PDF for print media
Once you know QR Code best practices, you must also know how not to use them.
For example—avoid putting the QR Code in a place with no access to mobile internet or Wi-Fi.
Or make sure it is neither too small nor too large to affect the scan ability adversely.
E. Real-world applications of QR Codes across industries
Here are some practical examples and case studies showcasing the power of QR Codes in various sectors:
1. Marketing & Advertising
Did you know?
40% of global QR Code scans are attributed to marketing campaigns
Source: ProfileTree
Case Study: L’Oreal’s Personalized Haircare Experience:
In 2021, L’Oreal used QR Codes on shampoo bottles and other products that linked to a personalized haircare routine recommendation tool.
The QR Code allows consumers and hairdressers to connect with the brand by discovering everything about the range’s hair diagnostics, products, ingredients, formulas, and packaging. This campaign increased customer engagement and brand loyalty.
Scanova’s Tip: If you have a brand, you use QR Codes on flyers or advertisements that link to exclusive discounts or coupons. By using unique trackable codes offered by Scanova, businesses can measure the effectiveness of their campaigns and understand customer behavior.
2. Retail
Case Study: Amazon Go’s cashier-less Shopping:
Amazon Go revolutionized retail with its grab-and-go model. Products have QR Codes that customers scan at self-checkout stations, offering a frictionless shopping experience. This showed how Amazon successfully leveraged QR Code technology to provide a seamless shopping experience to its customers.
Our checkout-free shopping experience is made possible by the same types of technologies used in self-driving cars: computer vision, sensor fusion, and deep learning. Our Just Walk Out technology automatically detects when products are taken from or returned to the shelves and keeps track of them in a virtual cart. When you’re done shopping, you can just leave the store. Shortly after, we’ll charge your Amazon account and send you a receipt
Amazon Announced in a Notification
Scanova’s Tip: Retailers can place QR Codes on clothing tags or product packaging that link to detailed descriptions, care instructions, or even customer reviews, empowering informed purchase decisions.
3. Manufacturing
Case Study: BMW’s Streamlined Production Process
BMW embedded QR Codes on car parts to track them throughout the assembly line. Their engines, air filters, and other parts have QR Codes on them to help and track with maintenance.
This ensures efficient production and facilitates quality control checks. Not just BMW, other big names like Toyota, Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz, and Ford have also started using similar QR Codes on their car parts for efficient tracking and management.
Scanova’s Tip: Manufacturers can place QR Codes on machinery with links to maintenance manuals, troubleshooting guides, or even spare parts ordering information, minimizing downtime and streamlining repairs.
4. Education
Case Study: The Metropolitan Museum of Art’s Interactive Exhibits
The Metropolitan Museum of Art (The Met) implemented QR Codes on artwork displays, linking to audio guides, historical background information, or even 3D models, enriching the visitor experience.
Both the Metropolitan Museum of Art and The Getty Museum have QR Codes available from their art collection and they use them to reach out to Animal Crossing (Nintendo game) fans.
Students are so tech-savvy nowadays that I believe it’s important to tap into that interest
Professor Steven, Division of Continuing Education, Harvard University
Scanova’s Tip: Teachers can incorporate QR Codes hidden around classrooms or within textbooks. Scanning these codes can lead to quizzes, interactive activities, or hidden learning resources, making education more engaging for students.
5. Tourism & Hospitality
Case Study: Singapore Tourism Board’s Interactive City Guide
Singapore deployed QR Codes at various tourist attractions. Scanning them provided visitors with interactive maps, historical information, or even augmented reality experiences, transforming sightseeing into an interactive adventure.
Another notable example is Springfield’s War Memorial QR Codes in Ohio. The QR Codes allowed visitors to learn more about what the monument memorializes. Visitors also got a chance to know more about the fallen heroes and veterans.
I control all of the codes from my computer. Also, I added pictures of all the people in the Purple Heart chapter and added pictures people gave, and notes to scan anything. I even put info for veterans to connect to other veterans.
Randy Ark
Back In 2010, The World Park hosted a tour of Central Park in New York. QR Codes were placed in various sites across Central Park. Scanning the Code enabled visitors to learn little-known information about the famed park.
Source: QRAnywhere
Scanova’s Tip: If you run a hospitality business you can leverage QR Codes for contactless check-in, allowing guests to bypass the front desk and access their rooms using their smartphones. This enhances convenience and streamlines the arrival process.
These are just a few examples of how QR Codes are impacting various industries. As technology evolves, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge, transforming the way we interact with information in the physical world.


F. Types of QR Codes
Say the content you want people to see is ‘target data’. Target data could be a website, a word in Spanish, your phone number, or even an image.
Classification of QR Codes depends on how this data gets encoded. There are two categories of Quick Response Codes:
1. Static QR Code
In a static Quick Response Code:
- Target data is encoded directly into the code, just like numeric data is encoded in a barcode
- The more information is encoded the ‘denser’ the Quick Response Code will become
- Encoding is permanent, which means that the target data can never be edited
- It is not possible to track scanning activity
Static QR Code can encode the following information in a structured format:
- URL
- Vcard (contact details)
- Text
- Wifi network access details
- Pre-loaded SMS
- Email address
- Phone number
- Calendar event
- Bitcoin wallet address
2. Dynamic QR Code
A Dynamic QR Code is a better way of encoding URLs in a QR Code. This confers it greater functionality and flexibility. In a Dynamic Quick Response Code:
- Target data can only be a URL
- The target URL is not stored directly in the Quick Response Code. Instead, a short URL (usually provided by the QR Code service) is encoded which redirects to the target URL
- It is possible to edit the encoded target URL at any time without the need to reprint the square barcode
- It is possible to track the scanning activity and get analytics
- You can ‘activate’ or ‘deactivate’ the Code at any time
Note that this categorization is based on how data is stored in a Quick Response Code. Based on the type of content, there can be many categories.
The number of categories of these 2D barcodes you can create depends upon the QR Code generator that you use.
Different generators offer different categories. For example, the Scanova QR Code generator allows you to create more than 20 types of Quick Response Codes.
To decide which type of QR Code you need to create, think about what action you want your target audience to take. For example, do you want them to:
1. See a website
2. See a text-based landing page
3. Listen to an audio
4. Make a payment using Paypal
5. Watch a video
6. Download a PDF
7. Follow you on social media
Once you decide what you want users to do, finalize the type of Quick Response Code you’ll create.
G. Generating a QR Code

Before you go ahead to create a QR Code, you must be clear about two things:
1. What do you want your audience to do
2. Which QR Code generator will suit your needs the best
A simple Google search on ‘QR Code generator’ will give you pages of results.
How do you then decide which service is the best for you? Will you compare all of them one by one?
Fret not! We’ve compiled a detailed comparison chart of the best QR Code Generator.
Why you should choose Scanova?
Out of all the competitors, Scanova has the most robust compliance with data security. It is GDPR compliant and is 27001:2013 ISO certified, so you know your data is in safe hands.
It allows you to measure the number of times your QR Codes are scanned and even connect this data with Google Analytics for more detailed insights. This information might be useful in determining the efficacy of your QR Code advertising.
Most importantly, Scanova is recognized for its user-friendly interface, which allows anybody to produce QR Codes without any technical knowledge.
The greatest part is that it gives exceptional customer service, assisting consumers if they run into problems or have queries regarding the platform or QR Code usage.
This attention to customer service improves the entire user experience and builds trust in the company. Investing in a strong QR Code generator with the necessary capabilities will build the basis for a successful and engaging QR Code campaign.
To add to it all, Scanova is trusted by many big brands.

Once you decide on which service you’ll use, there are three ways in which you can generate QR Codes:
1. By using an online QR Code Generator
There are many online QR Code generators such as Scanova, that help you create a Quick Response Code.
Here’s a step-by-step QR Code guide on how to use it:
1. Go to Scanova QR Code Generator
- Free Online Tool: This allows you to create 15+ different types of QR Codes for free.
- Scanova Account: If you require more features and frequent QR Code generation, consider signing up for a Scanova account (a free 14-day trial is available). This will grant access to additional functionalities and analytics.
2. Choose Your QR Code Type:
Scanova offers a variety of QR Code types depending on the information you want to encode.
3. Enter Your Information:
Once you choose the QR Code type, a dedicated field will appear for entering the relevant information. For example, if you select “Website URL,” paste the website address you want to link to.
4. Customize Your QR Code (Optional):
Scanova offers free and paid options for customizing your QR Code. You can even customize your Quick Response Codes by adding your brand color and logo.
- Add a Logo: Include your brand logo in the center of the QR Code for better recognition.
- Change Colors: Select custom colors for the foreground (data) and background to match your branding.
- Add a Call to Action: Include a short message like “Scan to Learn More” to entice users to scan the code.
5. Generate and Download Your QR Code:
Once you’ve entered your information and applied any desired customizations, click the “Create QR Code” button. Scanova will generate your QR Code. You can then download it as a PNG or SVG image file for use in print or digital media.
It is a fact that customized Quick Response Codes attract many more scans than standard black-and-white ones.
Hence, if your use case is promotional (such as marketing), and you want as many people to scan your QR Code as possible, you must customize it.
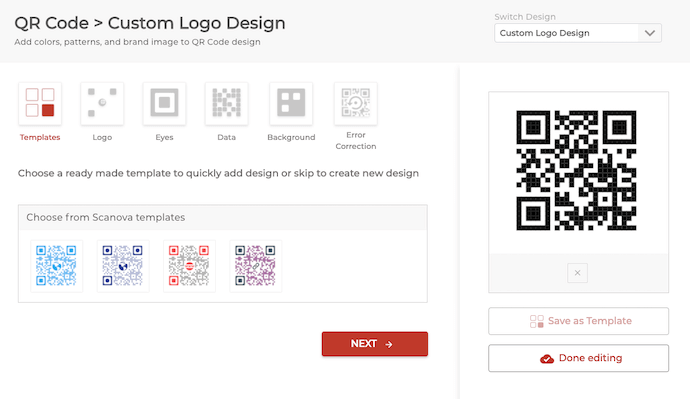
(Screenshot of Scanova Quick Response Code Generator)
2. Integrating QR Code API with your own system
If you have a mobile application or an information system that needs to generate these 2D barcodes, then you need a QR Code API.
It will integrate with your system and generate a Quick Response Code on demand.
3. Bulk Generation Services
Some QR Code service providers give the option of bulk generation (or batch generation).
This is helpful in case you need (say) 10,000 Quick Response Codes each with a unique ID.
You simply need to specify the data to be encoded in a spreadsheet, upload it to the bulk generator, add a design to the QR Codes (optional), and make payment.
Once your batch is ready, you can download it.
H. How to scan a QR Code
This can be done in either of the two ways mentioned below:
1. Using a QR Code scanning application on a mobile device
If you own a smartphone that has a camera, you can decode a Quick Response Code.
There are a number of QR Code scanning applications on all major app stores of iOS, Android, Windows, and Blackberry OS platforms.
Scanova’s Tip: i-nigma is one such application that works well on both iOS and Android, we highly recommend using it.
Also, as stated above, some smartphones now have inbuilt QR Code scanners. Check if your phone already has one.
2. Using a handheld or fixed optical scanner
You’ve seen scanners at the retail stores used to scan barcodes. Similarly, a handheld or fixed optical scanner can scan QR Codes.
These scanners are used when the scanning volume is higher in cases such as ticketing or mobile payments.
I. Advantages of QR Codes over barcodes
In technical terms, 2D barcodes have the following advantages over traditional barcodes:
1. Higher Capacity
A Quick Response Code can store up to 7,089 numeric characters (without spaces) or 2,953 alphanumeric characters with spaces.
Compare this with the capacity of barcodes i.e. 20 numeric characters (without spaces).
The higher capacity of QR Codes allows them to be used in various industries. From marketing, security, payments, and other solutions. Note that they can store web URLs, unlike barcodes.
2. Smaller Size
Compared to a barcode, a Quick Response Code can store more information in a smaller area of space.

This is helpful in inventory management as it is possible to print more QR Code labels in the same amount of space, saving printing costs.
For marketers also, this feature is extremely helpful as they usually have limited real estate on product packaging or promotional material.
See what should be the minimum size of your QR Code.
3. Damage Resistant
This is one of the primary reasons for QR Codes’ invention. The automobile industry used barcodes on spare parts. However, the factory environment resulted in wear and tear of the barcode.
This resulted in the barcodes being no longer scannable, causing delays and inefficiencies.
To avoid this, Denso Wave invented the QR Codes.
They can tolerate up to 30% of damage or dirt. This means—they remain scannable even if they’re up to 30% damaged.
This is possible due to a property called error correction.
Damage resistance allows personalization of QR Code design
You’ve probably noticed QR Codes with an image in the center as a logo.
It is the error correction that creates room for these 2D barcodes to be personalized. How?
To accommodate an image in the center, QR Code Generation tools introduce ‘damage’ by removing some square modules from the center of the QR Code.
The image (or the logo) can then be accommodated in the space created.

(These QR Codes were designed using Scanova)
4. 360-degree orientation
Unlike barcodes, a Quick Response Code is scannable from any angle. It has ‘eyes’ in three corners. Eyes help the scanning device determine its orientation.
This is useful as users do not have to rotate the Code (or themselves) to scan the code. Scanning here is much faster compared to barcodes.
5. Kanji Encoding
Unlike barcodes, QR Codes can encode information in JIS Level 1 and Level 2 Kanji character sets. This allows them to encode in a total of four encoding modes:
- Numeric
- Alphanumeric
- Byte/binary
- Kanji
This is to make it possible to encode single-byte languages (English) as well as double-byte languages (Japanese, Chinese, Korean).
These were the technical advantages of a Quick Response Code over a barcode.
J. Industry-wise QR Code best practices
QR Codes can be a powerful tool for various industries, but their effectiveness lies in following specific best practices. Follow these general best practices to make your QR Codes more efficient:
- Scannability: QR Codes must be easily scannable for a seamless user experience. Ensure a minimum size of 1 inch by 1 inch and high contrast with the background for clear readability.
- Placement: It is crucial to position them in well-lit, accessible areas. A QR Code will lose its purpose if the users have difficulty scanning them. Thoroughly test the code across various devices and lighting conditions before deployment.
- User Experience: Don’t leave users guessing! Include a clear call to action (CTA) that entices them to scan. This could be a simple “Scan for discount” or “Scan to learn more.”
- Mobile Optimized Landing Pages: The QR Code should always lead to relevant content optimized for mobile devices. To ensure smooth scanning, use short URLs that contain less data within the code itself.
Did you know?
United States leads the pack with 42.2% of all global QR Code scans. It is followed by India (16.1%), France (6.4%), the UK (3.6%), and Canada (3.6%).
Source: ProfileTree
K. Emerging trends in QR Code technology
QR Codes are experiencing a resurgence, and with that comes a wave of innovation. Here are some emerging trends that are pushing the boundaries of QR Code technology:
1. Interactive QR Codes and Augmented Reality (AR)
Imagine scanning a QR Code on a product package and seeing a 3D model come to life on your phone. Interactive QR Codes, when merged with Augmented Reality (AR), are blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. This can be used for product demonstrations, educational overlays on historical sites, or even interactive games.
2. Blockchain Integration
Blockchain technology is being explored to enhance the trustworthiness and transparency of QR Code-based systems, especially in supply chain management and product authentication. By recording QR Code scans on a blockchain ledger, it becomes possible to trace the entire lifecycle of a product from production to consumption, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeiting.
3. Micro QR Codes
While traditional QR Codes require a certain amount of space to be scannable, micro QR Codes are making a miniaturization revolution. These tiny QR Codes can be embedded on smaller objects like jewelry, business cards, or even inside pills for medication tracking.
4. Secure QR Codes with Encryption
Security is of the utmost importance, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Encrypted QR Codes are emerging as a solution. These codes add an extra layer of security by encrypting the data they contain, ensuring only authorized users can access the information upon scanning.
5. Integration with IoT Devices
QR Codes are increasingly being used to facilitate the setup and configuration of IoT devices. Instead of manually entering Wi-Fi credentials or device-specific information, users can simply scan a QR Code to establish a connection or configure settings, streamlining the onboarding process.
These are just a few of the exciting trends that are shaping the future of QR Codes. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications for these versatile tools.


H. FAQs
1. What is a QR Code? What does QR Code stand for?
A QR Code, short for Quick Response Code, is a two-dimensional barcode that stores data in a matrix of black squares on a white background. It was originally created in Japan in the 1990s for tracking automotive parts but has since become widely used for various purposes.
2. How does a QR Code work?
A QR Code works by encoding information such as text, URLs, contact details, or other data into a pattern of black squares and white spaces. When you scan a QR Code using a QR Code reader or a smartphone camera with QR Code scanning capability, the encoded information is quickly extracted and presented to the user.
3. What can QR Codes store?
QR Codes can store a wide range of data types, including:
– Website URLs
– Text
– Contact information (vCard)
– Geolocation coordinates, and much more
4. How do I scan a QR Code?
To scan a QR Code, you can use a dedicated QR Code scanner app, your smartphone’s built-in camera with QR Code scanning capabilities (most modern smartphones have this feature), or even some webcams on computers. Simply open the scanner app or camera, point it at the QR Code, and it will automatically recognize and decode the information.
5. What are QR Codes used for?
QR Codes have numerous applications, including:
– Marketing: Businesses use QR Codes on advertising materials to direct users to websites, promotions, or product information.
– Contactless Payments: QR Codes can facilitate mobile payments, allowing users to make transactions by scanning a code.
– Ticketing: Airlines, cinemas, and events often use QR Codes for electronic ticketing.
– Inventory and Asset Management: QR Codes are used in logistics and inventory management to track products and assets.
– Healthcare: QR Codes on medical records or prescriptions can provide quick access to patient information.
– Authentication: QR Codes can be used for two-factor authentication or to verify the authenticity of products.
6. Are QR Codes secure?
QR Codes themselves are not inherently secure or insecure. The security of the information they contain depends on what’s encoded within them. For instance, a QR Code containing a malicious website URL could lead to a security risk if scanned. Users should exercise caution and only scan QR Codes from trusted sources.
7. Can I create my own QR Codes?
Yes, you can generate your own QR Codes using Scanova. You input the desired data (e.g., a URL or text), and the generator creates a QR Code for you that you can save and share as needed.
8. Are QR Codes still relevant today?
Yes, QR Codes have experienced a resurgence in recent years, especially due to their contactless and touchless capabilities, which have become crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic. They continue to be widely used for various purposes, from restaurant menus to vaccination certificates.
9. Do I need special software to read QR Codes?
Most modern smartphones have built-in QR Code scanning functionality in their camera apps. If your phone does not have this feature, you can easily download a free QR Code scanner app from your device’s app store.
10. Are there different types of QR Codes?
Yes, there are different QR Code standards, such as QR Code Model 1 and QR Code Model 2. Additionally, there are variations like Micro QR Codes and High Capacity Color QR Codes, each designed for specific use cases and data storage capacities.
Keep in mind that QR Code technology continues to evolve, so it’s essential to stay updated on the latest developments and use cases for this versatile tool.
Conclusion
If you are still reading, you have covered all the basics of what a QR Code is.



Nice
This information was really helpful in my field of study. I was able to pick some few tips to help generate one to suit my purpose.
We’re glad you found it helpful.
This indeed was a very informative and detailed article…
Simply loved it!!!
Hey,
You can checkout our SDK tool for your use case. Here is the link: https://scanova.io/blog/qr-code-sdk/
This is very good and informative for QR code beginners
We’re glad you liked it.
Thank you
Thank you, i found it useful and informative !
We’re glad that you found it helpful.
realy make me undertand Qrcode, thank you for shared it.
We’re glad you found the article helpful.
Very good servise but it’s only known and understandable by few catagory.
Thanks for sharing this informative article, Gautam!
As a beginner, I found it really helpful in understanding what QR codes are and how they work. I also recently read the article on How to Use QR Codes in Salesforce and found it to be a great complement to your article.
Both pieces of content provided valuable insights on the practical applications of QR codes in the world of sales and marketing.
Keep up the great work!
Hey Kritik,
We are glad you found the article informative!
We’re having a RV event in July and would like to use QR Code to keep track of the participants (200+). Basic information would include name, address and vehicle location (in case of emergency).
Could a QR code work for us.
Hi Chris,
You could get in touch with our support team at [email protected]. They’ll let you know if this is possible.
Thanks!