Types of QR Codes Explained (2026 Guide with Examples & Uses) | Scanova

In a nutshell:
- 30+ types of QR Codes exist today, from static links to complex GS1-based codes
- There are two broad categories: Static and Dynamic QR Codes. The difference lies in editability and tracking
- QR Code formats include Model 1, Model 2, Micro QR, iQR, Frame QR, and GS1 QR Codes
- Dynamic QR Codes support analytics, password protection, and multi-URL redirection
- A quick comparison of QR Codes vs Barcodes reveals QR Codes are more versatile, data-rich, and interactive
Quick Response (QR) Codes have evolved from industrial tracking tools to essential digital connectors that bridge the physical and digital worlds.
Originally developed by Denso Wave in 1994 for tracking automobile parts, these versatile types of QR Codes now facilitate everything from restaurant menus to trillion-dollar payment systems.
Understanding the different types of QR Codes and QR Code formats available today is crucial for businesses and individuals looking to leverage this powerful technology.
Whether you need static QR Codes for permanent links or dynamic QR Codes for flexible campaigns, this comprehensive guide explores every major QR format and application.
Let’s begin!
A. QR Code vs Barcode: What’s the difference?
The fundamental advantage of QR Code formats over traditional barcodes lies in their two-dimensional data encoding. This allows information storage both horizontally and vertically.
Ultimately, this enables QR Codes to hold significantly more data while remaining readable from any angle, but they differ in terms of design, information capacity, and applications.
Here are the key differences between QRs and barcodes:
1. Design
- QR Codes: QRs are square-shaped and consist of black squares arranged on a white background. They also have three smaller squares in the corners that help scanners identify the orientation of the code.
- Barcodes: Barcodes are typically linear, consisting of parallel lines of varying thickness and spacing. They can be one-dimensional (1D) or two-dimensional (2D), with 1D barcodes being more common in traditional retail settings.
2. Information capacity
- QR Codes: QRs can store much more information compared to traditional barcodes. They support a variety of data types, including alphanumeric characters, binary data, and special characters. This makes them suitable for encoding URLs, contact information, and multimedia content.
- Barcodes: Traditional 1D barcodes can encode a limited set of numeric or alphanumeric characters. 2D barcodes have higher information capacity than 1D barcodes but are generally not as versatile as QRs.
3. Data encoding
- QR Codes: QRs use a matrix pattern to encode data, allowing them to store information both horizontally and vertically.
- Barcodes: Barcodes use variations in the width and spacing of parallel lines to represent data in a linear format.
4. Readability
- QR Codes: QRs can be read from any angle and have error correction capabilities, allowing for successful scanning even if the code is partially damaged or obscured.
- Barcodes: Traditional 1D barcodes require a clear line of sight for accurate scanning. 2D barcodes may offer some error correction, but their readability can still be affected by damage or distortion.
5. Applications
- QR Codes: QRs are widely used in various applications, including marketing, advertising, product packaging, ticketing, and mobile payments. They excel in interactive and dynamic content delivery.
- Barcodes: Barcodes are commonly used in retail for inventory management, pricing, and product identification. They are prevalent on product labels and packaging.
6. Scanning devices
- QR Codes: QRs can be scanned using smartphones, tablets, and specialized QR scanners. Many modern smartphones come equipped with built-in QR scanning capabilities.
- Barcodes: Traditional 1D barcodes are typically scanned using laser-based scanners, while 2D barcodes may require specialized 2D barcode scanners.
| Feature | QR Codes | Traditional Barcodes |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Square matrix with 3 corner markers | Linear parallel lines |
| Data Capacity | Up to 7,089 characters | 20-25 characters maximum |
| Scanning Direction | 360-degree omnidirectional | Horizontal line-of-sight required |
| Error Correction | 30% data recovery capability | Limited to no error correction |
| Mobile Compatibility | Native smartphone camera support | Requires specialized scanners |
| Content Types | URLs, text, multimedia, payments | Numeric product identification |
| Update Capability | Dynamic codes can be edited | Static, unchangeable |
| Cost | Free generation tools available | May require proprietary systems |
B. QR Code format types: Explained in simple terms
QR Codes come in different styles, each built for a specific job.
1. Model 1 QR Code
This is the original version of the QR Code. It was the first to be created, but it is rarely used today.
- Holds up to 1,167 characters
- Includes 3 finder patterns to help scanners
- Supports only basic error correction
- Now considered outdated
2. Model 2 QR Code
This is the version you see almost everywhere now, from posters to packaging to Google Maps QR Codes.
- Can store over 7,000 numbers or around 4,200 alphanumeric characters
- Comes in versions 1 to 40, depending on data size
- Has better error correction – up to 30% of code can be damaged and still work
- Used for menus, links, apps, and more
- It’s the current international standard (ISO/IEC 18004)
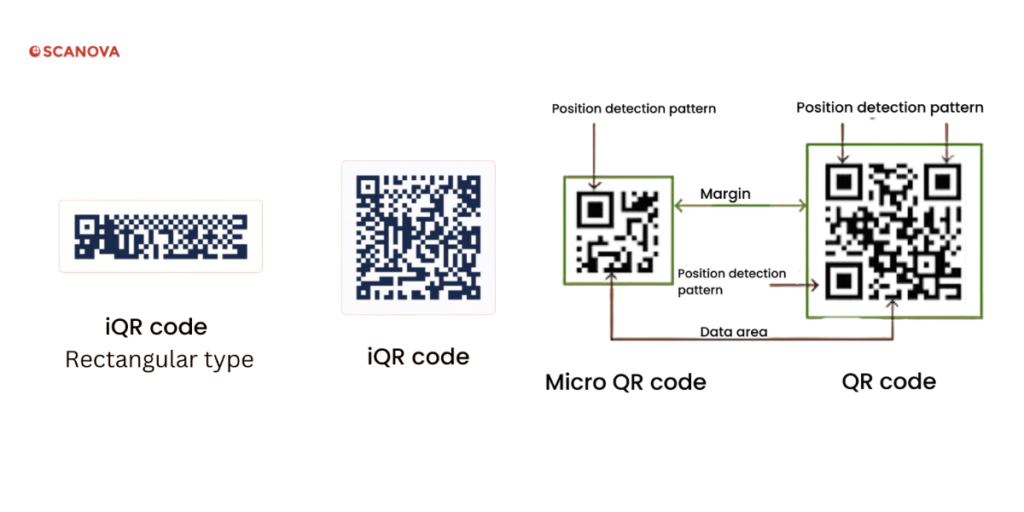
3. Micro QR Code
This one is made for small spaces. Think pill bottles, cables, or mini labels.
- Very compact: starts as small as 11×11 modules
- Holds up to 35 characters
- Uses just one finder pattern
- Saves space but holds less info
- Great for tight packaging areas
4. iQR Code
This is the flexible one. It can be square or rectangular, and it stores a lot more data than standard QR Codes.
- Comes in 61 square and 15 rectangular versions
- Holds thousands of characters
- Can be up to 30% smaller than regular QR Codes
- Has a higher error correction level (up to 50%)
- Ideal for ads, marketing, or high-volume print jobs
5. SQRC (Secure QR Code)
Need to store private info? This format is made for that.
- Looks like a normal QR Code, but has a secure layer
- Can store confidential data like passwords or health info
- Common in banking and healthcare
- Not readable by regular QR scanners (needs special reader)
6. FrameQR
Want a QR Code that blends into your design? This is the creative version.
- Has a central space (called a canvas) for logos, pictures, or messages
- Still scans like a regular QR Code
- Perfect for marketing campaigns or branded packaging
- Combining style and function
7. GS1 QR Codes
This is the new standard for retail and product tracking, backed by GS1 and Project Sunrise.
- Stores product info like GTIN, expiry, batch, etc.
- Helps with traceability and inventory management
- Can be scanned by both shoppers and checkout systems
- Expected to replace barcodes in many stores by 2027
- Already supported by 82% of retailers and 92% of brands
- Learn more on GS1.org
8. HCC2D Code (Prototype)
This is still a work in progress, but it may be the future.
- A new kind of 2D code
- Aims to improve data storage and scanning
- Could bring exciting features down the line
- Not yet available for public use
So, Model 1 vs Model 2 QR Codes: What’s the Difference?
- Model 1 is the original format. It can store around 1,167 characters. It works fine, but it is now outdated.
- Model 2 is what most QR Codes use today. It can store over 7,000 numbers or around 4,200 letters and numbers. It also handles scanning errors better and is easier to read from all angles.
That’s why Model 2 has become the international standard, according to the team that invented QR Codes – Denso Wave.
Quick Recap of Specialized QR Codes:
- Micro QR Code: Small and simple. Best for tight spaces.
- iQR Code: High-capacity and flexible. Great for printed materials.
- SQRC: Keeps private data secure. Used in finance and healthcare.
- FrameQR: Designed for style. Adds logos and branding to the code.
- GS1 QR Code: Built for retail and logistics. Tracks products globally.
Each type exists for a reason. Picking the right one depends on what you’re trying to do.
C. Applications of QR Codes

QR Codes play a significant role in driving website traffic. Users can be sent directly to a webpage by merely scanning the code, providing easy access to the desired content.
You can use static QR Codes and dynamic QR Codes as per your use case. The basic difference between a dynamic and static QR Code is that a dynamic QR Code can be edited after creation, while a static QR Code cannot. Hence, static QR Codes are also called permanent QR Codes.
1. Drive Traffic to Website
QR Codes are used to drive website traffic as a simple yet effective method. By embedding a website URL in a QR Code, users can scan it with their mobile device and be taken directly to your site.
It eliminates the need to manually type in a web address, reducing potential errors and making the process quick.
You can even use a multi-URL QR Code if you have various websites.
This is particularly effective for printed media, where embedding clickable links is impossible. From posters to business cards and product packaging, these QR Codes instantly bridge physical media and your online presence.
2. Navigate to your location
Physical navigation becomes a breeze with location QR Codes, Google Maps QR Codes, and Waze QR Codes.
By scanning the QR Code, the user’s mobile device can launch a navigation app (like Google Maps or Waze) and provide directions to the desired location.
Creating a location QR Code can be a game-changer for businesses with physical locations. For example, retail stores, event venues, or restaurants. It also provides a way to guide people directly to places of interest, increasing footfall.
3. Deliver downloadable contact details
QR Codes can also carry contact information within them. These are called vCard QR Codes. When scanned, they show a landing page with details such as your name, mobile, website, company, designation, weblinks, and even a profile picture.
Plus, the page also has a ‘Save as Contact’ button. Hence, the recipients can easily save your contact with a simple click. No need for them to type anything. Easy, right?
4. Deliver documentation
QR Codes can contain links to PDF files, which can be downloaded and stored later. This is a practical solution for businesses that must share documents, manuals, reports, or e-books with their customers or stakeholders.
Businesses can also use an Excel QR Code generator like Scanova to optimize and fine-tune their business operations and more.
To deliver documentation, you can use a QR code for a Word document or Google Docs.
A PDF QR Code can be printed on product packaging or advertising material, giving users quick and easy access to information. QR Codes can significantly enhance customer experience and engagement, helping businesses share knowledge and add value.
You can also convert a PowerPoint presentation into a QR Code.
5. Promote your app
App Download QR Codes are programmed to direct users to app download pages on the App Store or Google Play.
Google link to QR Code also comes in handy. This means businesses can promote their apps simply by distributing these app deep link QR Codes on their marketing materials.
They can use a business QR Code generator such as Scanova for their use case. For a region-specific use case, you can use multilingual QR Codes.
Businesses can increase their app’s visibility and usage by making it easier for people to find and download their app. That means enhanced customer engagement and loyalty.
6. Welcome guests safely
In the age of contactless services, Restaurant QR Codes have become a critical tool. By using a Menu QR Code, restaurants can allow guests to view menus, place orders, and make payments without touching common surfaces.
To ease the process further, you can automatically generate QR codes for each guest and use them to authenticate entries.
This reduces the risk of viral transmission and streamlines the ordering process, providing an enhanced dining experience. Something to explore while deciding on the marketing strategy of your restaurant.
7. Improve conversion rates
Landing Page QR Codes help you design a mobile landing page even if you don’t have a website. Here, you may add text, images, video, weblinks, etc.
Businesses often use it to create pages with the objective of converting them into customers.
When people scan the QR Code, they are taken to the required landing page where they may make a purchase, sign up for a service, or perform any other desired action.
8. Engage users with video content
Video QR Codes allow businesses to share video content directly with their customers. When users scan a YouTube QR Code, they are taken to a video on YouTube.
This provides businesses with a unique way to engage customers, sharing anything from product demonstrations and tutorials to promotional videos and testimonials.
9. Increase visual appeal
Image Gallery QR Codes allow businesses to share a range of images with their customers. Retail businesses can use this type of QR Code to showcase various products, and real estate companies can use it to display pictures of their properties.
When a user scans an Image Gallery QR Code, they can swipe through a range of images, providing a visually engaging experience.
10. Instantly share MP3 files
QR Codes can unlock a world of auditory experience by sharing MP3 files. For instance, musicians can make their work accessible by getting fans to scan a QR Code to instantly stream a new song, album, or playlist.
Podcast creators can also use QR Code podcasts to share episodes. At the same time, educators might incorporate QR Codes for audiobooks into learning materials to provide audio lessons.
These audio QR Codes are readily available, offering a user-friendly way to share audio even via print media.
11. Deliver deals and offers
For many businesses, coupon QR Codes are an effective strategy to drive sales and customer engagement.
These QR Codes can contain information about a special discount, a limited-time offer, or exclusive deals. Hence, they encourage customers to take advantage of the offer.
The codes can be added to store displays, product packaging, digital platforms, etc.
12. Share relevant content
With text QR Codes, users share information that might not fit comfortably in print media.
They can be used in a multitude of settings, from education and information dissemination to marketing and promotions.
QR Code for GPS location can be used to make the marketing strategy better.
For example, they can provide supplementary info about a museum exhibit, instructions for product assembly, or additional content about a book or article.
13. Receive feedback
Rating and feedback QR Codes streamline the process of collecting customer feedback.
By scanning a QR Code form, customers can rate their experience, provide suggestions, or voice complaints. Hence, businesses get to know vital information to improve their services or products.
These QR Codes can be positioned on receipts, product packaging, or in-store displays, providing a simple and accessible way for customers to share their thoughts and experiences.
Businesses can enhance customer engagement and satisfaction by making the feedback process interactive and easy.
14. Make event planning easier
Event QR Codes simplify the management and promotion of events. They can hold all the necessary details about an event.
For example, location, date, time, schedule, and even a link for ticket purchases or registration.
By scanning the code, attendees can easily access all the information they need, saving time and avoiding confusion.
Event organizers can also update the content behind the QR Code in real-time, ensuring attendees always have the latest information.
15. Cashless payments
Payment QR Codes are an essential part of the growing trend towards cashless transactions. They are fast and secure, making the payment process smoother for businesses and customers.
Users scan the QR Code with their smartphone, enter the amount, and authorize the payment.
16. Make calls instantly
Call QR Codes can streamline communication by enabling users to make a phone call by simply scanning a code.
These can be particularly helpful in business settings, allowing potential customers to reach out for inquiries immediately.
Imagine a real estate sign with a QR Code that, when scanned, initiates a call to the agent.
This makes contacting the appropriate person quick and convenient, improving the user experience and engagement.
Additionally, businesses can also pair QR Codes with call center software to track customer inquiries and improve response times.
17. Send instant messages
Much like Call QR Codes, Message QR Codes allow for instant communication, only this time in text format.
By scanning the code, users can instantly generate a preformatted text message or email, ready to send to a specified recipient.
This is useful in providing better customer service, allowing users to send feedback, place orders, or make inquiries with just a few taps on their mobile devices.
18. Save personal information
MeCard QR Codes offer an efficient way to share and save personal information. Like a digital business card, these encrypted QR Codes hold information such as a person’s name, phone number, email, and address.
This information can be instantly saved to the user’s contact list when scanned. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, reducing errors and improving efficiency, especially in professional networking scenarios.
19. Connect to Wi-Fi fast
Wi-Fi QR Codes are a secure and efficient solution to the often cumbersome process of connecting to Wi-Fi networks.
Instead of verbally sharing or manually entering complex Wi-Fi passwords, these QR Codes can be scanned to connect to a specific network instantly.
This is especially useful in public spaces like coffee shops, libraries, or hotels, improving the user experience by offering a quick and hassle-free connection method.
Application-Specific QR Code Types
| QR Code Type | Primary Use | Industry | Key Features | Scan-to-Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| URL QR | Website Links | Marketing, Retail | Direct web access, Landing pages | Visit Website |
| vCard QR | Contact Sharing | Business, Networking | Complete contact info, Auto-save | Save Contact |
| Wi-Fi QR | Network Access | Hospitality, Events | Auto-connect, Secure protocols | Connect to Wi-Fi |
| Payment QR | Transactions | Finance, Retail | Mobile wallets, Secure payments | Make Payment |
| Menu QR | Digital Menus | Food Service | Contactless ordering, Real-time updates | View Menu |
| PDF QR | Document Access | Education, Business | Instant downloads, Manuals | Download File |
| Video QR | Media Content | Marketing, Education | Product demos, Tutorials | Play Video |
| Location QR | Navigation | Real Estate, Events | GPS coordinates, Turn-by-turn | Get Directions |
| App QR | Software Download | Technology, Gaming | Store links, Cross-platform | Download App |
| SMS QR | Text Messaging | Customer Service | Pre-filled messages, Support | Send Message |
| Email QR | Communication | Business, Support | Pre-filled emails, Inquiries | Send Email |
| Social QR | Social Media | Marketing, Personal | Profile links, Follow actions | Follow/Connect |
| Coupon QR | Promotions | Retail, Marketing | Discounts, Special offers | Redeem Offer |
| Event QR | Calendar | Events, Business | Meeting details, RSVP | Add to Calendar |
| Audio QR | Sound Content | Entertainment, Education | Music, Podcasts, Audio guides | Play Audio |
D. Static vs Dynamic QR Codes: Understanding the difference!
Not all QR Codes work the same way. The biggest difference comes down to two types: Static and Dynamic.
1. What is a Static QR Code?
A Static QR Code holds fixed data, like a URL or contact info, that can’t be changed once it’s created.
- You can’t update the link later
- You don’t get scan tracking or analytics
- Great for simple uses like business cards, event posters, or print menus
- It’s free and easy to use
2. What is a Dynamic QR Code?
A Dynamic QR Code gives you more flexibility.
- You can edit the link anytime, even after printing
- You can track scans, when, where, and how often
- You can add extra features like password protection, expiry dates, or multi-link redirects
- Best for marketing, campaigns, or anything that may change later
So, which one should you use?
If your link is permanent and you don’t need stats, go with Static.
If you want control, edits, and insights, choose Dynamic. It’s that simple.
E. How to create a QR Code for your business?

Several factors come into play when selecting a QR Code generator for your business. These include the generator’s ease of use, the types of QR Codes it can produce, its design options, and whether it provides dynamic QR Codes.
You should also have the option to generate dynamic QR Codes in bulk. The generator should also offer tracking and analytics to measure your QR Code’s effectiveness.
We recommend going ahead with Scanova. It allows you to create more than ten types of QR Codes and some handy customization options.
Here’s a quick and easy way to do it using Scanova’s QR Code Generator:
Step 1: Copy your Website URL
Go to your website, click the address bar, and copy the full URL (e.g., https://yourwebsite.com )
Step 2: Choose a QR Code Generator
Pick a reliable tool like Scanova. It’s beginner-friendly and offers both static and dynamic QR Codes with customization options.
Step 3: Create the QR Code
- Visit Scanova’s website and select the ‘Website URL’ category.
- Paste your link and click Continue.
- Name your QR Code for easy access later.
- Choose Dynamic (recommended) if you want to edit the link later or track scans.
- Click Create QR Code.
Step 4: Customize the design
Make your QR Code stand out:
- Add your logo or a short label
- Match colors to your brand
- Change patterns, shapes, or add a frame with a call-to-action like “Scan to Visit”
Pro Tip: A well-designed QR Code receives more attention and is scanned more often than a simple black-and-white one.
Keep in mind that Scanova needs you to register for a free trial to access the advanced customization tools. Check out Scanova’s pricing information.
Step 5: Download and Test
Once you’re happy with the design:
- Click Download (you’ll need to sign up for a free trial)
- Choose high-res formats like PNG or SVG
- Test the QR Code by scanning it with your phone

And that’s it! You’ve got a custom QR Code ready to share on your website, flyers, packaging, or social media.
F. What are the best types of QR Codes to use?
The best type of QR to use depends on the specific purpose or information you want to convey.
Here are some common types of QRs and their best use cases:
1. Website URL QR Code
- Best For: Website links, landing pages, and online content
- Use Case: Direct users to a specific webpage or online resource
2. Text QR Code
- Best For: Encoding plain text information
- Use Case: Share messages, notes, or any alphanumeric text efficiently
3. vCard QR Code
- Best For: Business cards, email signatures, or any context where contact information is shared
- Use Case: Easily share contact details by scanning the code
4. Email QR Code
- Best For: Encoding an email address, subject, and body text for pre-filled emails
- Use Case: Simplify the process of sending emails to a specific address
5. Phone number QR Code
- Best For: Business cards, advertisements, or any scenario where contact by phone is desired
- Use Case: Users can quickly call a number by scanning the phone number QR Code
6. SMS QR Code
- Best For: Encoding predefined SMS via QR Codes
- Use Case: Prompt users to send a specific text message by scanning the code
7. Wi-Fi QR Code
- Best For: Encoding Wi-Fi network credentials for easy device connection
- Use Case: Simplify the process of connecting to a Wi-Fi network
8. Geolocation QR Code
- Best For: Sharing geographic coordinates
- Use Case: Provide directions or lead users to a specific or live location on a map
9. Event/Calendar QR Code
- Best For: Encoding event details such as title, date, time, and location
- Use Case: Add events to calendars by scanning the Calendar QR Code
10. Payment QR Code
- Best For: Mobile payments and transactions
- Use Case: Allow users to make payments by scanning the code with a mobile payment app
11. App Store QR Code
- Best For: Encoding links to apps on app stores
- Use Case: Direct users to download or view apps
G. Why do business marketers choose QR Codes over other barcodes?
Business marketers often choose QRs over other traditional barcodes for several reasons, as QRs offer distinct advantages that align with modern marketing strategies and consumer behavior.
Here are some key reasons why business marketers prefer QRs:
1. Versatility and information capacity
- QR Codes: QRs can store a variety of data types, including text, URLs, contact information, and more. This versatility allows marketers to convey more information and engage users with multimedia content, such as videos or images.
- Traditional Barcodes: Traditional barcodes primarily encode numerical data and lack the flexibility to convey diverse information.
2. Easy scanning with mobile devices
- QR Codes: QRs can be easily scanned using smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices equipped with cameras. This aligns well with the widespread use of mobile technology.
- Traditional Barcodes: They often require specialized barcode scanners, limiting accessibility.
3. Enhanced user engagement
- QR Codes: QRs enable interactive and engaging experiences for users. Marketers can use QRs to link to websites, social media pages such as Twitter, videos, or promotional content, fostering a deeper connection with the audience.
- Traditional Barcodes: Traditional barcodes typically provide basic product identification and lack the interactivity of QRs.
4. Cost-effectiveness
- QR Codes: Generating QRs is cost-effective, and many online tools offer free QR code creation. There’s no need for additional hardware or software.
- Traditional Barcodes: Implementing traditional barcodes may require specialized equipment and software, which can be more expensive.
5. Dynamic content updates
- QR Codes: QRs can link to dynamic content that can be updated without changing the printed code. This flexibility is useful for time-sensitive promotions or changing information.
- Traditional Barcodes: Traditional barcodes are typically static and don’t support dynamic content updates.
6. Marketing analytics
- QR Codes: Scanova provides analytics, allowing marketers to track the performance of their QR campaigns. This includes data on scan rates, locations, devices used, and more.
- Traditional Barcodes: Traditional barcodes generally lack built-in analytics capabilities.
7. Print and digital integration
- QR Codes: QRs seamlessly integrate with both print and digital media. They can be included in print materials like brochures or posters and shared digitally through email or online channels.
- Traditional Barcodes: Traditional barcodes are primarily used in retail and physical product packaging.
8. Wider range of applications
- QR Codes: QRs find applications in various industries, including retail, marketing, education, healthcare, 3PL solutions, logistics, and more. They can be used for diverse purposes beyond inventory management.
- Traditional Barcodes: Traditional barcodes are commonly associated with inventory and product identification in retail settings.
H. FAQs: Types of QR Code
1. How many different QR Codes are possible?
The number of possible QRs is extremely large, as the QR code format allows for a wide range of configurations and data sizes.
The number of possible QR codes can be calculated based on the different combinations of modules (black and white squares) within the code.
QRs come in different versions and sizes. The version of a QR defines its size, with larger versions capable of storing more data. Each version can have different error correction levels as well.
The error correction level determines how much redundant information is included in the QR to tolerate errors and damage.
2. How many types of QR Codes are there?
QRs come in various types, categorized as static and dynamic. Static QRs include URL codes for website links, text codes for plain text information, and specialized codes for WiFi connections, emails, contacts, geolocations, phone numbers, SMS, and events.
Dynamic QRs offer additional functionality, such as editability, analytics tracking, multi-URL redirection, password protection, and time sensitivity. Customization options include colored QRs and those incorporating logos.
With their versatility, QRs cater to diverse needs, allowing for efficient encoding of information ranging from simple text to complex data, making them widely applicable across industries and purposes.
3. What are the two types of QR Codes?
The two primary types of QRs are static QR Codes and dynamic QR Codes.
I. Static QR Codes
- Characteristics: These QRs contain fixed, unchangeable information.
- Use Cases: Commonly used for straightforward data like website URLs, text, contact information, WiFi network details, and more.
- Limitations: Once generated, the encoded information cannot be modified without creating a new QR Code.
II. Dynamic QR Codes
- Characteristics: These QRs allow for flexibility and can be edited or updated after creation.
- Use Cases: Ideal for scenarios where the encoded information may change, such as marketing campaigns, promotions, or dynamic content like event details.
- Advantages: Offers features like analytics tracking, the ability to redirect to different URLs based on conditions, and the option for time-sensitive content.
4. Are any 2 QR Codes the same?
The probability of two randomly generated QRs being the same is extremely low. The uniqueness of QRs is a result of the vast number of possible combinations and configurations they can have.
The QR standard includes different versions, sizes, and error correction levels, contributing to a large space of potential QR variations.
However, it’s important to note that the uniqueness of QRs relies on their random generation and adherence to the QR standards. If a QR is manually generated with specific data, the chance of generating an identical QR increases.
In practice, QR generation tools and algorithms are designed to produce unique codes for different sets of data.
The risk of unintentional collision (two different sets of data producing the same QR Code) is considered extremely low due to the complexity of the encoding process and the large space of possible configurations.
5. What is the most common type of QR Code?
The most common type of QR is the standard static QR Code that typically contains a URL.
These types of scan codes are widely used for various purposes, including marketing, advertising, and providing convenient links to websites.
When people scan these QRs with their smartphones or other devices, they are directed to the encoded URL, which could lead to a product page, promotional offer, or any other online content.
Static QR codes with URLs are popular due to their simplicity and ease of use. They are easily generated and widely supported by QR reader apps on smartphones.
Businesses often use them for connecting users to their websites, online resources, or specific landing pages, making them a prevalent choice for a broad range of applications.
6. Is a QR Code 1D or 2D?
A QR is a two-dimensional (2D) matrix barcode. Unlike one-dimensional (1D) barcodes that consist of parallel lines of varying widths, a QR Code is a square or rectangular pattern of black squares arranged on a white background.
The information in a QR is encoded both horizontally and vertically, allowing it to store a significant amount of data compared to traditional 1D barcodes.
The term “2D” signifies the two-dimensional nature of QR Codes, distinguishing them from the linear structure of 1D barcodes.
Summing Up
QR Codes are growing fast, and they’re not going anywhere.
From simple static codes that hold fixed info to advanced dynamic codes that let you track scans and update links, each type serves a purpose. They’ve become a must-have tool for businesses, marketers, and even everyday users.
In 2025 alone, people scanned QR Codes over 41 million times – that’s a 433% jump in just four years. Clearly, more people are using them every day.
As new QR Code formats and uses keep popping up, it’s important to know which type works best for your needs.
Whether you’re running a campaign, sharing a product, or streamlining a process, picking the right QR Code makes all the difference.
Now’s the time to try them out. Use the format that fits your goal, and make the most of this smart way to connect the physical world with the digital one.

