QR Code Structure: Everything you need to know
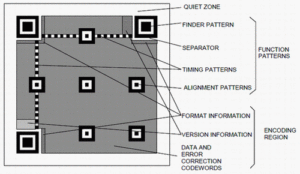
You have probably seen black & white square-shaped barcodes on magazine ads or business cards. These are QR Codes. They do the job of connecting you from print media to useful online content. But have you ever wondered about the QR Code structure? How is a QR Code scanner able to read it?
After reading this guide, you will become an expert on how QR Code structure.
QR Code structure
Think of a QR Code as a language. Humans can’t read this language but mobile devices and scanners can.
Just as the English language has rules on how to form a sentence, a QR Code is also made up of elements.
Here’s a sneak peek on how it works:
In addition, the illustration below can also help you out. It depicts the basic structure of a QR Code and its elements:

QR Codes are made up of data modules
A Module is the fundamental unit of a QR Code. They are the black-and-white blocks that make up the data encoded in a QR Code.
Modules store data and make up the rows and columns of the QR Code (called the Data Matrix). Positioning of data bits begins from the bottom right corner of the matrix. It moves upward in a two-module wide column and switches direction on reaching the top.
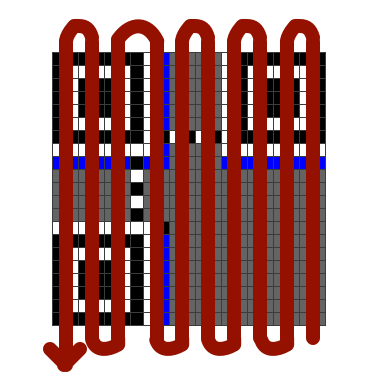
Number of rows and columns of modules are determined by the Version Number
A QR Code has equal number of rows and columns of modules (square-shaped). But QR Codes cannot have any number of rows (or columns). The number depends on the Version Number of the QR Code. For example:
- Version 1 have 21 rows and 21 columns of modules
- Version 2 have 25 rows and 25 columns, and so on
- And Version Number ranges between 1 and 40.
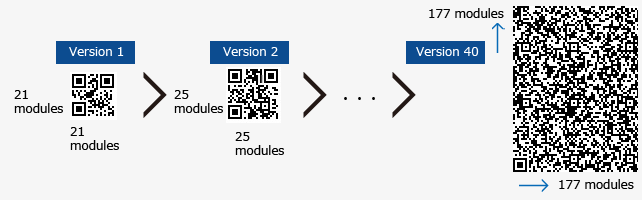
Higher the version number, higher the number of rows and columns. Thus, higher is the storage capacity.
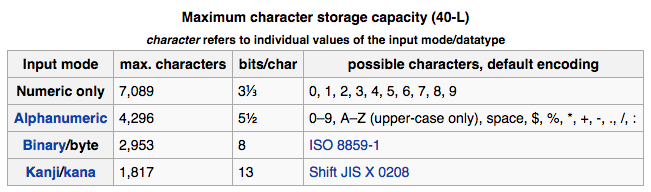
Data can be encoded in four-character modes
It is possible to encode data in a QR Code in four modes – numeric, alphanumeric, binary, and Kanji. Storage capacity differs depending upon version number and encoding mode.
Size of the module is determined by Timing Pattern
The sixth row and column make up the Timing Pattern. These are alternating black-and-white modules. These enable the scanning software to understand the width of a single module.
Scanner identifies the QR Codes via Finder Patterns
Unlike barcodes, QR Codes have Finder Patterns (also called Position Markers or Eyes). These take up three corners of the code. Their function is to help scanners recognize the QR Code accurately and allow them to read the QR Code at high speed.
They are mainly responsible for identifying a QR Code and its orientation.
Separator distinguishes finder patterns and data
A separator helps the scanner distinguish between Finder Patterns and the actual data.
A QR Code needs a Quiet Zone to be identified
A QR Code must have white space (equal to 4 modules thick) called a Quiet Zone around the boundary of the QR Code.
It helps the scanner to locate the Finder Patterns.
Alignment markers determine the orientation of the QR Code
The Alignment Markers are smaller than position markers. They help the scanner determine the orientation of the QR Code. This makes it possible to scan a QR Code at any angle.
Format Information is also required to decode the QR Code
Format information contains two pieces of data – Level of Error Correction and Mask Pattern.
Error Correction allows wear & tear
A QR Code has the capability to remain scannable even if it is somewhat damaged – up to 30%. This is possible due to an algorithm called Reed-Solomon Error Correction. CDs and DVDs also use this algorithm to remain readable despite scratches, wear & tear, etc.
Note that adding Error Correction increases the number of modules (data blocks) in a QR Code. Hence, it is possible to adjust the level of Error Correction as per requirements.
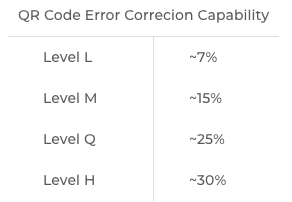
There are four possible levels of error correction:
- L–7%
- M–15%
- Q–25%
- H–30%
You may have noticed that some QR Codes have images in them as part of their design. This is possible because designers add the image as an error.
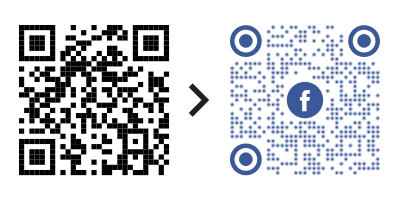
The custom QR Code, created using Scanova, will still remain scannable and functional.
Mask Patterns make QR Codes more readable for the scanners
Masking is inverting the colors of the modules. Dark modules convert to white and white ones to dark.
Data Masking is a way of choosing the best possible arrangement of modules. This makes it easy for scanners to decode the QR Code.
There are eight Mask Pattern possibilities. For example:
- Mask every even-numbered row for Mask Pattern 1
- Mask every third column for Mask Pattern 2
Here is how to choose the right masking pattern:
- Apply all eight mask patterns to the QR Code
- Calculate Penalty Score for each resulting QR Code
- Choose the arrangement with the least Penalty Score
What information is in a QR Code
QR Codes have the capacity to store three key types of information: size, error correction levels, and data types.
When considering the size, a QR Code can consist of up to 177 rows and 177 columns, with a potential of 31,329 data modules. However, typical QR Codes are often smaller. The size directly corresponds to the QR Code’s version, which ranges from the smallest version 1 (21 rows by 21 columns) to the largest version 40 (177×177).
Additionally, it’s important to note that the minimum size of a QR Code is typically determined by the scanning distance rather than the data size.
Regarding error correction levels, QR Codes are encoded with one of four levels, determining their ability to withstand damage while remaining scannable. The higher the correction level, the more robust the QR Code is. This acts as a stored backup. Lower correction levels allow for more space for size and data.
In terms of data types, QR Codes can store up to 7,089 numeric characters or 2,953 alphanumeric characters, with the ability to hold bytes and kanji, although these are less commonly used. These figures are based on the lowest error correction level.
Practically, QR Codes find applications in various areas such as business cards, restaurant table QR Codes, authentication, hotel check-ins, website logins, contactless payments, digital menus for wines and food, and more.
Notably, the amount of information a standard one-dimensional barcode can contain ranges from around 20 to 100 characters, highlighting the superiority of QR Codes across numerous industries in terms of data storage and quick accessibility.
Moreover, the complexity of a QR Code doesn’t necessarily increase in direct proportion to the amount of information it holds, as this distinction is evident between static and dynamic QR Codes.
Storage capacity of a QR Code
QR Code can store up to 7089 digits or 4296 characters, including special characters. This is more than the capacity of barcodes and makes it possible for QR Codes to store massive information.
Scannability
QR Code’s scannability largely depends on its elements’ color and the background’s color. It is mandatory to ensure sufficient contrast between the two.
How to scan a QR Code
Now you know how a QR Code works. So, the next question is—how to scan one?
To scan it, you need to follow these basic steps:
1. Open your smartphone’s camera (in case it has a QR code scanning feature inbuilt) or a third-party QR Code scanning app
2. Hold the camera in front of the QR Code
That’s it. You’ll receive the notification once it gets scanned. It’s just like clicking a picture.
How to make the most of the QR Codes
Here is how you can leverage QR Codes:
1. Direct traffic to your website
Say you want to take people to your website. It could be for any use case such as:
- Watching a video
- Checking out your product range
- Making a purchase
To do it, you probably will add a link to the appropriate webpage on your promotional creatives. But here’s the problem—end-users will have to pull out their smartphones, open the browser, tediously type the link, and finally visit your website. This is a long process. While some people may do it, others won’t bother doing it.
But a Website URL QR Code can help you accomplish this feat easily. Simply add it to your promotional materials, and end-users can scan it to visit your website. After all, the easier the process, the better are the conversions (website visits here).
2. Gain social media followers
The importance of social media presence has become essential for both an individual and a business. But you can’t hope people will search your TikTok username social media handle and follow you online.
What you can rather do is use a Social Media QR Code. When scanned, it shows all your social media platforms such as Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter. End-users can then select their favorite platform to follow you online.
3. Share contact information
Networking is an integral part of the professional world. And when you meet people, you probably give them your name card in the hope that they’ll connect with you. But that’s not enough.
Recipients have to pull out their smartphones to open their contacts app and type all your details to finally save you as a contact. This needs them to put effort. Hence, no wonder why most business cards end up in the trash rather than in the recipient’s phone.
But just putting up a QR Code on the card can increase the likelihood of them actually saving your contact.
It’s called a VCard QR Code. Recipients scan it to see your contact details on their phones with a button—Save as Contact. Hence, it removes the need for them to manually type your details. A simple scan is all they need to do.
4. Provide event information
Say you are organizing an event and need to inform your audience about it. An Event QR Code can help you do it.
Your audience can scan it to see your event’s complete information including exact venue location, timing description, and images. And in addition to it, they also get the option to RSVP.
5. Share documents
Sharing documents among friends, colleagues, or customers is common. It can be reports, PowerPoint presentations, or product details. And a Document QR Code can help you do it. Your audience just needs to scan it to access the encoded document.
6. Boost app downloads
Do you have a mobile app for your use case? You know getting people to download your mobile app can be quite a task. But an App Store QR Code can help you here. When scanned, the QR Code redirects the end-users to your app on the app store based on their mobile’s OS. They can then download the app and start using it.
7. Offer discounts and coupons
You know how valuable coupons and discounts are. They help attract customers and ultimately lead them to make a purchase. But customers don’t like remembering random characters.
This is where a Coupon QR Code can help you. When scanned, customers can redeem the coupon to avail its benefit.
Best Practices
Here are some of the best practices that you must know regarding QR Codes:
1. Add an appropriate CTA
CTA translates to ‘Call-to-action’. It is a small instruction that tells the users what action they need to do. And this kind of small text nudges them to take the required action.
It could be anything such as ‘Scan here to visit our website’ or ‘Scan here to download our app’.
2. Add a design to the QR Code
If you are planning to use QR Codes for promotions, consider adding design to them. That’s because they are visually appealing and can grab the recipient’s attention.
As a matter of fact, custom QR Codes attract 50%-200% more scans than plain black-and-white ones.
3. Test scan the QR Code
It is always advisable to test scan the QR Code before putting them out for your target audience.
4. Choose optimal printing format
It’s recommended to use QR Codes in vector formats such as SVG, EPS, and PDF if you’re going to use them for print media creatives. They ensure that the QR Code doesn’t get pixelated even after you zoom in or zoom out.
FAQs: QR Code structure
1. What is the structure of a QR Code?
A QR Code is composed of a grid of black squares on a white background. It typically consists of three main parts: the finder patterns, the alignment patterns, and the timing patterns. These elements help scanners detect and interpret the QR Code’s content accurately.
2. What are the finder patterns in a QR Code?
Finder patterns are the square patterns located at three corners of the QR Code. They help the QR Code scanner detect and orient the code. Finder patterns consist of a specific arrangement of black and white modules that enable the scanner to identify the QR Code’s size and alignment.
3. What are the alignment patterns in a QR Code?
Alignment patterns are smaller square patterns present within the QR Code. They assist with precise positioning and alignment during scanning. These patterns are especially useful in large QR Codes to ensure accurate reading, even if the code is slightly distorted or skewed.
4. What are timing patterns in a QR Code?
Timing patterns are a series of alternating dark and light modules that run through the QR Code’s rows and columns. These patterns help in determining the scanning speed and facilitate the correct interpretation of the QR Code data by the scanning device.
5. What is the format information in a QR Code?
Format information in a QR Code refers to the data that defines the QR Code’s specifics, such as error correction level and mask pattern. This information is essential for the correct decoding of the QR Code data and ensuring its accuracy, even in the presence of potential errors or distortions.
6. How does the data area of a QR Code work?
The data area of a QR Code contains the actual encoded information, which can include various types of data, such as text, URLs, contact information, or other specific data formats. This area is where the QR Code stores the information that will be retrieved when the code is scanned.
7. What is the structure of a QR Code, and how does it function in data encoding?
A QR Code is like a digital puzzle that holds information in a compact, scannable format. Its structure has three main parts: finder patterns, data modules, and alignment markers.
The square finder patterns in the corners help your phone or scanner locate and orient the code.
The data modules—the tiny black and white squares—store the actual information, such as a URL, text, or contact details. The alignment markers ensure the code can be scanned even if bent or distorted.
What makes QR Codes special is their ability to store data horizontally and vertically, unlike traditional barcodes, which only store data in one direction.
This two-dimensional design lets them pack much more information in a small space. When you scan a QR Code, your device reads the patterns and converts them into readable data.
Thanks to built-in error correction, it’s fast, efficient, and works even if part of the code is smudged or damaged. Cool, right?
8. How does the QR structure impact its readability and scanning efficiency?
The clever design of a QR Code makes it super easy to scan and read, even in less-than-ideal conditions. Its structure is built for efficiency. The finder patterns—those big squares in three corners—make it quick for scanners to locate and align the code, no matter the angle.
Even if the code is tilted or upside down, the scanner can understand it. The alignment markers come into play when the QR Code is on curved or uneven surfaces, like a bottle or a box, ensuring the scan stays accurate.
Then there’s the error correction feature, like a safety net. Even if part of the QR Code gets scratched, dirty, or obscured, it can still be read because the code stores extra bits of data to recover the missing pieces.
Plus, the dense layout of data modules (those tiny squares) allows for high-speed scanning and processing of large amounts of data in a flash. This combination of clever design and robust features makes QR Codes reliable and lightning-fast to scan.
9. What is the formula for QR Code generation, and how is the structure of QR Code determined?
Creating a QR Code combines data encoding, error correction, and pattern placement in a structured way.
The process begins with the information you want to store, like a URL or text. Depending on the content type, this data is converted into a binary format using specific encoding modes such as numeric, alphanumeric, byte, or Kanji.
Once encoded, error correction data is added using a mathematical formula based on Reed-Solomon algorithms. This ensures the QR Code can still be read even if parts of it are damaged.
The structure of the QR Code—like its size and the arrangement of black and white modules—is determined by its version and error correction level. QR Codes come in 40 versions, ranging from a small 21×21 grid (Version 1) to a massive 177×177 grid (Version 40).
The more data you want to store, the larger the version you’ll need. Finder patterns, alignment markers, and timing patterns are added to specific grid positions to guide the scanner.
All these elements work together to create a QR Code optimized for readability, resilience, and speedy scanning.
10. How does the structure of QR Code ensure data integrity and error correction?
The structure of a QR Code is designed with built-in safeguards to keep your data safe and readable, even when things go wrong. Its error correction capability is at the heart of this, and Reed-Solomon algorithms power it.
This system adds redundant data to the QR Code during the encoding process. Think of it like packing spare puzzle pieces in case a few go missing—this redundancy ensures the QR Code can still be decoded accurately, even if up to 30% of it is damaged, smudged, or obscured.
Additionally, the finder patterns, alignment markers, and timing patterns play key roles in ensuring that scanners can quickly locate and correctly interpret the code, even if it’s distorted or on a curved surface.
The QR Code’s grid structure also ensures that data is distributed across the entire code rather than concentrated in one area. This way, even if one part of the code is damaged, the rest can fill in the gaps.
These features make QR Codes highly reliable and perfect for real-world use where wear and tear or imperfect scanning conditions are common.
Still have a question about QR Code structure? Ask in the comments below.
{ “@context”: “http://schema.org”, “@type”: “VideoObject”, “name”: “How do QR Codes Work: Explained in Minutes”, “description”: “You are probably familiar with the black & white square-shaped barcodes. You might have seen them at billing desks, product packagings, or even on tent cards in restaurants. 00:00 – Introduction 00:17 – How do QR Codes Work These are called QR Codes. They connect the offline media with online content. RESOURCES And LINKS Scanova QR Code Generator: https://bit.ly/36m3dFX How do QR Codes Work (article): https://bit.ly/34VDZhd And you are wondering—how do these QR Codes work? Well, first you need to think of a QR Code as a language that mobile devices and scanners can read but humans can’t. Just as every language has some letters or words to form a sentence, a QR Code has elements. And this video explains all the elements of a QR Code and how they contribute to its functionality: First, Data modules. They are the black-and-white blocks of a QR Code. They store all the information which is shown to the end-users. The positioning of data bits begins from the bottom right corner of the matrix. It moves upward in a two-module wide column and switches direction on reaching the top. This makes the rows and columns of the QR Code Second, Eyes or the Finder patterns. They are the big squares at the corners of the QR Code. They allow the scanners to recognize the QR Code accurately and allow them to read it at a high speed Third, Separator. It helps the scanners differentiate Finder Patterns from the actual data Fourth, Quiet Zone. It is the white space equal to 4 modules around the boundaries of the QR Code. It helps the scanners locate the Finder Patterns Fifth, Alignment Markers. They are smaller than eyes. And their role is to help the scanners determine the orientation of the QR Code. This helps scan the QR Code at any angle which gives it 360-degree scannability Sixth, Error-correction. It ensures that QR Code remains scannable even after getting damaged or dirty by up to 30%. This happens via algorithm called Reed Solomon Error Correction. It increases the number of modules (data blocks) in the QR Code. Hence, it’s possible to adjust error correction which has four levels: L–7%, M–15%, Q–25%, and H–30% At last, Mask Patterns that make QR Codes more readable for the scanners. Masking is inverting the colors of the modules, that is, dark modules convert to white and vice versa There are eight mask patterns available in total and the right one is chosen based on the one with least penalty score. Now you know how a QR Code works and comes live within 2 seconds of holding a smartphone in front of it. Note that each QR Code can store up to 7,089 numeric or 4296 alphanumeric characters. And it’s important for a QR Code to have high contrast with the background for good scannability. In case, you want to know how to scan a QR Code, just open your smartphone’s camera and hold it in front of the QR Code. You’ll receive a notification when it gets scanned. In case your phone doesn’t have in-built QR Code scanning feature, you can install any free third party QR Code scanning app to do the job. That’s it. In case you’re looking forward to creating a QR Code, you can try Scanova for free. Log on to scanova-dot-io. The link is in the description. If you found the video helpful, hit the like button. And don’t forget to subscribe to our channel. The ‘must watch’ playlist on QR Code Basics: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLFfkNvrqjcSn-5Sm-vN2dDvoVRQEK674u Connect with Scanova on other social media platforms – Website – https://bit.ly/3DTIp3F LinkedIn – https://in.linkedin.com/company/scanova Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/scanovatech/ #QRCode #ScanovaQRCode #Scanova #QRCodes #QR”, “thumbnailUrl”: “https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pamazHwk0hg/default.jpg”, “uploadDate”: “2022-02-21T15:45:03Z”, “duration”: “PT3M45S”, “embedUrl”: “https://www.youtube.com/embed/pamazHwk0hg”, “interactionCount”: “12045” }